Java内部类使用总结
Categories: Java; Tagged with: Java • 内部类; @ February 13th, 2009 20:44顶层类只能处于Public跟默认访问级别. 而内部类可以处于任意访问级别.
A 实例内部类:
- 在创建实例内部类实例时, 外部类的实力必须已经存在.
- 实例内部类自动持有外部类实例的引用
- 一个外部类可以有多个内部类 因此不允许外部类直接调用内部类方法或属性. 而内部类进对应一个外部类, 因此可以直接使用外部类的引用.
- 在实例内部类中不能定义静态成员, 只能定义实例成员.
- 当内部类与外部类有同名的成员时,如age, 在内部类中直接使用age或this.age表示inner2内age 而OnlyForTest.this.age表示外部类中的age.
B 静态内部类:
- 静态内部类的实例不会自动持有外部类的特定实例的引用, 因此在创建内部类的实例时, 不必创建外部类的实例.
- 静态内部类可以直接访问外部类的静态成员, 如果要访问外部类的实例成员, 就必须通过外部类的实例去访问
- 静态内部类中可以定义静态成员和实例成员
- 客户类可以通过完整的类名直接访问静态内部类的静态成员.
局部内部类:
- 与局部变量一样, 不能被访问控制符修饰.
- 只能在当前方法中使用
- 不能包含静态成员
- 在局部类中定义的内部类也不能被访问控制符修饰
- 局部内部类和实例内部类一样, 可以访问外部类的所有成员, 此外, 局部内部类还可以访问所在方法中的final类型的参数和变量.
匿名类:
- 匿名类没有构造方法, 但是会调用父类的构造方法.
- 匿名类尽管没有构造方法, 但是可以在匿名类中提供一段实例初始化代码
- 除了可以在外部类的方法内定义匿名类之外, 还可以在生命一个成员变量时定义匿名类
- 匿名类除了可以继承外, 还可以实现接口
- 匿名类和局部内部类一样, 都可以访问外部类的所有成员, 如果匿名类位于一个方法中, 还可以访问方法内部的final类型的变量和参数
举例[实例内部类, 静态内部类]:
public class OnlyForTest {
public static String staticOutMember = "Static Out Member";
private String userName;
private int age;
//省略Getter/Setter
public static void main(String[] args) {
OnlyForTest oft = new OnlyForTest();
//A1. 在创建实例内部类实例时, 外部类的实力必须已经存在.
OnlyForTest.Inner inner = oft.new Inner();
//A3. 一个外部类可以有多个内部类 因此不允许外部类直接调用内部类方法或属性, 在需要时, 使用内部类实例访问内部类成员
//而内部类进对应一个外部类, 因此可以直接使用外部类的引用.
oft.age = oft.new Inner2().age;
inner.setOutInstanceNmae("tom");
oft.new Inner2().print();
//B1: 直接访问静态类静态成员, 不需创建实例.
System.out.println(staticInnerClass.staticInnerMember);
new staticInnerClass().printNmae();
}
class Inner {
public void setOutInstanceNmae(String s){
//A2. 实例内部类自动持有外部类实例的引用
userName = s;
System.out.println("内部类直接引用外部类实例 - 内部类赋值外部类成员 " + userName);
}
}//end of class Inner
class Inner2 {
int age= 2;
//A4. 在实例内部类中不能定义静态成员, 只能定义实例成员.
//报错!static int staticInt = 4;
public void print() {
System.out.println(userName);
//A5. 当内部类与外部类有同名的成员时,如age
//直接使用age或shis.age表示inner2内age
//OnlyForTest.this.age表示外部类中的age
System.out.println(age);
System.out.println(OnlyForTest.this.age);
//B2. 直接访问外部类的静态成员
System.out.println(staticOutMember);
}
}//end of class Inner2
static class staticInnerClass {
public static String staticInnerMember = "Static Inner Member";
public void printNmae() {
//B3:静态内部类在访问外部类实例变量时, 必须通过外部实例
OnlyForTest o = new OnlyForTest();
o.userName = "set by Static Inner Class";
System.out.println(o.userName);
}
}//end of staticInnerClass
}
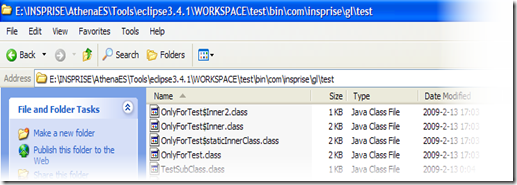
编译后的Class文件:
DeCompiler之后 Inner的构造函数:
OnlyForTest$Inner2()
{
this$0 = OnlyForTest.this;
super();
age = 2;
}
可见, 每个inner实例都会自动包含一个外部类OnlyForTest的引用
而staticInnerClass类的构造函数为空, 因此他的实例不会自动引用外部类
从Decompile的Class文件来看, 对JVM来说, 无所谓内外类之分, 他们都是Class, 只是内部类会自动引用外部类实例 或是 其他特定的功能而已.
Servlet实践 2-2
Categories: Java; Tagged with: Java • Servlets; @ February 13th, 2009 20:24|
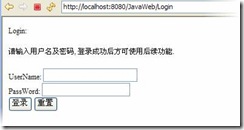
Login设计 |
|
当Request进入时, 先通过request.getSession(false)检查Session是否存在, 如果存在则表明已经登录,则通过sendRedirect(Calc.URL_MAIN)跳转到主页面 response.sendRedirect(); |
package com.insprise.servletStu;
//省略import
public class Login extends HttpServlet {
public static final String USER_NAME = "userName";
public static final String PASS_WORD = "passWord";
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
private static final String INPUT_USER_NAME = "inputUserName";
private static final String INPUT_PASSWORD = "inputPassWord";
private String passWord;
private String name;
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
name = (String) getServletContext().getAttribute(USER_NAME);
passWord = (String) getServletContext().getAttribute(PASS_WORD);
HttpSession session = request.getSession(false);
if (session != null) {
response.sendRedirect(Calc.URL_MAIN);//如果已经登录后再次打开登录页面, 跳转到主界面
return;
} else {
response.setContentType("text/html");
response.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
PrintWriter out = response.getWriter();
if (request.getParameter(INPUT_USER_NAME) != null) {
String inputUserName = request.getParameter(INPUT_USER_NAME);
String inputPassWord = request.getParameter(INPUT_PASSWORD);
if (inputUserName.equals(USER_NAME) && inputPassWord.equals(passWord)) {
request.getSession().setAttribute(Calc.CURRENT_USER, USER_NAME);
response.sendRedirect(Calc.URL_MAIN);
return;
} else {
//登录失败
}
} else {
//省略若干println…
}
//省略doPost
}
|
|
CalcListener实现 |
|
该类实现ServletContextListener接口, 在Application初始化时, contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent sce)方法会被自动呼叫, 在此之后, Filter与Servlet开始初始化. 使用getServletContext().getInitParameter()方法获得web.xml中<context-param>标签中的内容. 使用ServletContext的setAttribute方法为获得用户名及密码, 并作为Attribute加入到ServletContext中 重要方法: ServletContext. setAttribute(); |
public class CalcListener implements ServletContextListener {
private static Logger log = Logger.getLogger(CalcListener.class);
public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent sce) {
log.info("Context Started!" + sce.getServletContext());
ServletContext context = sce.getServletContext();
Calc.MAX_CALCULATION_TIMES_PER_SESSION = Integer.parseInt(context.getInitParameter(Calc.MAX_CALCULATIONAS_PER_SESSION));
Calc.MAX_CALCULATION_TIMES_PER_SESSION = Integer.parseInt(context.getInitParameter(Calc.MAX_CALCULATIONAS_PER_SESSION));
//读取到用户名及密码, 加入到Context Attribute中
context.setAttribute(Login.USER_NAME, new String(context.getInitParameter(Login.USER_NAME)));
context.setAttribute(Login.PASS_WORD, new String(context.getInitParameter(Login.PASS_WORD)));
}
}
|
2.4 抓图
Servlet实践 2-1
Categories: Java; Tagged with: Java • Servlet; @ February 13th, 2009 20:21实践
2.1 需求及用例
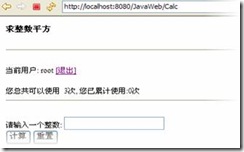
创建一个简单的计算器, 当用户输入整数时, 输出其平方值. 但用户需要登录才能进行操作, 用户的登录信息放在web.xml中, 每次登录用户可以使用该计算器三次, 三次使用结束后, 提示用户推出后重新登录继续使用.
|
User Case 用例 |
登录系统 |
||
|
Brief description |
登录系统 |
||
|
Scope/Level |
AthenaES/User goal |
Primary actor/role |
Root |
|
Minimal & Success Guarantees 保证 |
Minimal: The system logs how far it may get |
||
|
Preconditions 前提 |
无 |
||
|
Triggers 引发条件 |
用户打开登录界面 |
||
|
Main Success Scenario 成功场景 |
1. 系统提示用户输入用户名及密码 |
||
|
Extension 扩展 #1 |
3a: 系统无法核实用户身份, 提示其用户名或密码错误, 并提示用户重新输入 |
||
|
Notes and Issues |
无 |
|
User Case 用例 |
计算平方 |
||
|
Brief description |
计算平方 |
||
|
Scope/Level |
AthenaES/User goal |
Primary actor/role |
Root |
|
Minimal & Success Guarantees 保证 |
Minimal: The system logs how far it may get |
||
|
Preconditions 前提 |
Actor is logged in |
||
|
Triggers 引发条件 |
用户点击”计算” |
||
|
Main Success Scenario 成功场景 |
1. 确认用户使用次数未达到上限 |
||
|
Extension 扩展 #1 |
1a: 用户使用次数达到上限, 系统提示用户重新登陆后继续使用 |
||
|
Extension 扩展 #2 |
4a: 系统检测到用户输入不合法, 系统提示用户重新输入 用户重新进行2~4 |
||
|
Notes and Issues |
无 |
2. 2 数据分析:
1. ServltContext层次的数据: 由于用户名及最大限制次数等信息在整个Servlet进程中都会被使用, 因此使用Context的Listener来实现.
2. Session层次的数据: 用户本次登录已使用次数应记录在Seesion中, 在当前Session中使用
3. Request层次的数据: 用户输入的数值尽在当前Request中使用
2. 3 具体实现
|
Calc主页面实现: |
|
首先检查Session是否存在, 不存在则跳转到登录界面. |
package com.insprise.servletStu;
//省略import
public class Calc extends HttpServlet {
public static final String MAX_CALCULATIONAS_PER_SESSION = “maxNumber”; // 最大使用次数的Key
public static int MAX_CALCULATION_TIMES_PER_SESSION; // 最大使用次数
public static final String CURRENT_USER = “currentUser”; // 当前用户
public static final String URL_MAIN = “./Calc”; // 主页面
public static final String URL_LOGIN = “./Login”; // 登录页面
public static final String URL_LOGOUT = “./Logout”; // 注销页面
private static final String ACCESS_COUNT = “accessCount”; // 使用次数
private static final String INPUT_INT = “inputInt”;
private static Logger log = Logger.getLogger(Calc.class);
private static final int MAX_INT = 46340; // Math.sqrt(Integer.MAX_VALUE)
private HttpSession session;
private Integer accessCount; // 使用次数
public void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws IOException, ServletException {
session = request.getSession(false);
if (validatUser(session)) { // 已登录
accessCount = (Integer) session.getAttribute(ACCESS_COUNT);
if (accessCount == null) { // 如果Session中不存在accessCount, 则表明其为新登录用户,
// 赋值为0;
accessCount = 0;
session.setAttribute(ACCESS_COUNT, accessCount);
}
if (checkUseTimes(accessCount)) { // 已登录, 且使用次数在限制之内, 进行操作.
proccessRequet(request, response);
} else { // 已登录, 但使用次数操过限制,提示用户重新登陆.
accessOverTime(request, response);
}
} else { // 未登录
response.sendRedirect(URL_LOGIN);
}
}
public void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws IOException, ServletException {
doGet(request, response);
}
// 检查用户是否已登录
private boolean validatUser(HttpSession s) {
if (session != null) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
// 检查用户使用次数是否超过限制
private boolean checkUseTimes(Integer number) {
//省略
}
// 使用次数超过限制之后 提示其登录;
private void accessOverTime(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws IOException {
request.getSession().invalidate();
response.getWriter().println("本次登录已使用完毕, 请重新登录");
return;
}
// 获得输入数值, 计算结果, 返回信息
private void proccessRequet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws IOException {
Integer i;
String title = "求整数平方";
response.setContentType("text/html");
response.setCharacterEncoding("utf-8");
// 不使用缓存 在点击推出后 按后退按钮时 不会出现缓存中的内容.
response.setHeader("Cache-Control", "no-store");
response.setDateHeader("Expires", 0);
response.setHeader("Pragma", "no-cache");
PrintWriter out = response.getWriter();
out.println(ServletUtilities.headwithTitle(title));
out.println("" + title + "
");
out.println("当前用户: " + session.getAttribute(CURRENT_USER) + " [退出]
");
String numberString = request.getParameter(INPUT_INT);
if (numberString != null) {
try {
out.println(" " + i + " 的平方是: " + calculator(i) + "
");
log.info("累计第[" + accessCount + "]次使用, 本次计算的参数为: " + i);
} catch (Exception e) {
out.println("您可能输入的不是整数 或您输入的整数绝对值过大
请输入: 一个绝对值小于" + MAX_INT + " 的整数
");
}
}
out.println("您总共可以使用 " + MAX_CALCULATION_TIMES_PER_SESSION + "次, 您已累计使用:" + accessCount + "次
");
// 最后一次运行时, 停止输出Form;
if (accessCount.equals(MAX_CALCULATION_TIMES_PER_SESSION)) {
out.println("已达到最大使用次数限制, 请退出后重新登陆");
return;
}
printForm(out);
out.println("");
}
// 计算
private int calculator(int i) {
accessCount = new Integer(accessCount.intValue() + 1); // 使用次数增加一次
session.setAttribute("accessCount", accessCount);
return i * i;
}
// 打印一个Form
private void printForm(PrintWriter out) {
out.print("